Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) defines a protocol that aims to simplify data transfer between network elements. Here SNMP AGENTS (= SNMP SERVER (GCore)) provide a certain set of variables that reflect the status of the network element (e.g. router, server, switch, printer, computer).
The variables can be queried and also influenced by (with the corresponding access rights for the variable value) the SNMP MANAGER (=SNMP CLIENT). While the SNMP AGENT is passive in the situation just described and waits for a query for one or more values from the manager, it is also possible for the SNMP AGENT to send a message into the network. This message is called an SNMP TRAP. When the SNMP AGENT is configured, it is defined to which devices the trap should be sent.
The following scenarios are possible with SNMP:
-
Monitoring of network components
-
Remote query, remote control and remote configuration of network components
-
Error recognition and reporting
For G-Core/Diagnostics to be SNMP capable, the following files are required: GCoreDiagnosticsSnmp.dll and GCoreDiagnosticsSnmpNamespace.dll. These must be in the G-Core directory. The file GBMIN.mib is in the same directory. This file is required for the SNMP manager. It is not required for the functionality of G-Core/Diagnostics.
Installation of the Windows SNMP Agents
Windows operating systems already contain an SNMP Agent. If the SNMP Agent is already installed, then the entry SNMP Service can be found in the Windows system services.
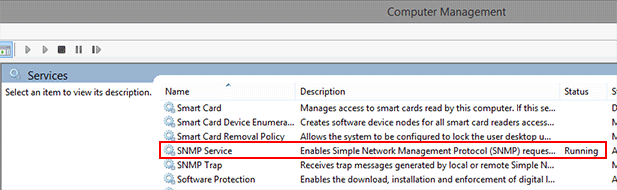
If there is no such entry, the SNMP service must be installed via Programs and Features:
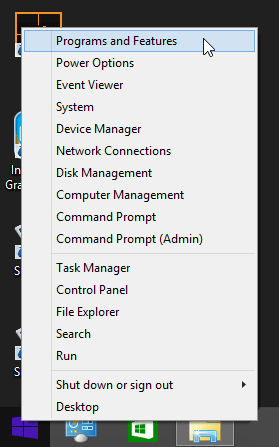
Add or Remove Programs > Add/Remove Windows Components > SNMP.
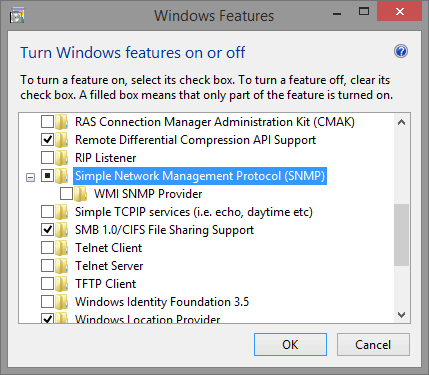
After successful installation, the SNMP service can be found in the Windows services.
It is now possible to establish a connection from an SNMP manager to the Windows SNMP agent and query information about the computer. During this procedure the basic information of the Windows operating system is made available.
SNMP Agent and Extension Agents
In addition to the basic information, it is possible to use the Windows SNMP Agent to make data from other programs (in our case, G-Core/Diagnostics) available for an SNMP manager.
So that the SNMP Agent can make this additional information from G-Core/Diagnostics available, the file "GCoreDiagnosticsSnmp.dll" must exist in the G-Core directory. At the runtime of G-Core/Diagnostics the following registry keys are set. When G-Core/Diagnostics is stopped these keys are automatically deleted again. This is normal and necessary behavior.
The following key must be set in the Windows registry when G-Core/Diagnostics is running:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters\ExtensionAgents]"GCoreDiagnostics"="SOFTWARE\Geutebrueck\Gng\GCoreDiagnostics\SNMP\CurrentVersion"
and
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Geutebrueck\Gng\GCoreDiagnostics\SNMP\CurrentVersion]"PathName"="%gngpath%\GCoreDiagnosticsSnmp.dll"
Windows SNMP Configuration
After installation and registration of the extension Dlls, as part of the configuration it can be determined which machines can access the SNMP Agent and to which devices traps are sent. This is performed in the property dialog of the SNMP Service. (Accessed in the Windows services, right click on SNMP Service > Properties.
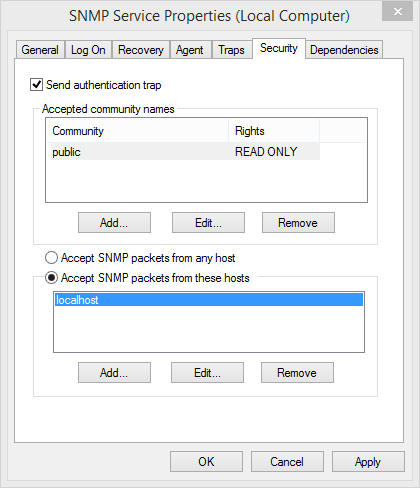
In the tab Security of the property dialog you set which computers in the network can send queries to the SNMP agent. The lower section is decisive. Either all IPs are allowed (Accept SNMP packages from any host) or you can specify which computers can send a query to the SNMP agent (Accept SNMP packages from these hosts). In the latter case, the IP addresses of the querying hosts be must listed explicitly.
In the tab Traps it is specified to which computers an active message should be sent by the SNMP agent. The computers that are to receive a trap must be listed here explicitly.
G-Core/Diagnostics does not currently support traps. For this reason, these settings are not important at this time.