Windows and NTP
As already mentioned, Microsoft still used SNTP under Windows 2000. For the previous versions of Windows, some software companies developed their own programs for time synchronization under Windows.
However, for modern authentication systems, such as those used in Windows 2000 and newer versions a time stamp is required. Therefore, NTP was introduced for use in the Windows environment.
For all setup work for an NTP client or NTP server, you must be logged on as an administrator.
Setting Up the NTP Client XP and 2000
In Windows XP, time synchronization was set up using Control Panel > Date and Time. After clicking on the tab Internet Time you could specify the server name (for example, ntp.rz.tu-harburg.de).
In Windows 2000 the configuration of time synchronization was performed by the W32Time service. To do so, you needed start a console with Start > Run > CMD.
In the console, the following was entered:
-
net stop w32time<ENTER> -
net time /setsntp:ntp.rz.tu-harburg.de<ENTER> -
net start w32time<ENTER>
You could also write a batch file and add it to the autostart menu. Contents of the batch file would be, for instance net tim \\servername /set /yes, where a valid server was specified with "servername".
Setting Up an NTP Server in NT, 2000 and XP
-
Start the registry editor (Start > Run > Regedit) and look for the entry
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControllSet\Services\ LanmanServer\Parameters. -
Right-click with your mouse in the right window and in the context menu that appears, click New/DWORD value.
-
For Windows 2000 and XP the entry should be:
[New Value #1] REG_DWORD 0x00000000(0) -
For Windows NT, the entry would then be:
[New Value #1] 0x00000000(0)
-
-
Rename the new value to TIMESOURCE.
-
After the value has been created and renamed, you must enter the correct value for the DWORD value. Select the newly created value by right-clicking. In the context menu, click Modify.
→ The Edit DWORD Value properties window opens.
-
Select the base Hexadecimal and then replace 0 with 1 in the Value field.
-
Confirm the entry with OK. Close all programs and restart Windows.
-
To check the time server, start the console (cmd.exe or command.com).
-
In the console enter the command
net timeand press Enter. If the name of the local computer is returned, setting up the time server is complete.-
In XP, the time server receives its value from the settings described above under Date and Time.
-
For NT and 2000, you must use the console. Then type the command: net time /querysntp. If return is something similar to servername,01, then everything is fine.
If you receive an error message that the computer is not configured to use a specific SNTP server, then the time server must be set. In the console enter the command
net time /setsntp:time.windows.com(for the SNTP server from windows.com) ornet time /setsntp:"time.windows.com lancom.workgroup"(for two different time servers, which are separated by using a space character between them).
-
Windows 7
With the current Windows version Windows 7 it is possible to run the computer as either an NTP client and or an NTP server. It is necessary to set up the computer as an NTP server for a closed system that does not have access to a (Internet) time server.
In Windows 7, there are a number of restrictions that make it difficult to configure an NTP client or an NTP server. You can find the configuration dialogues in the Group Policy Editor under Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Windows Time Service.
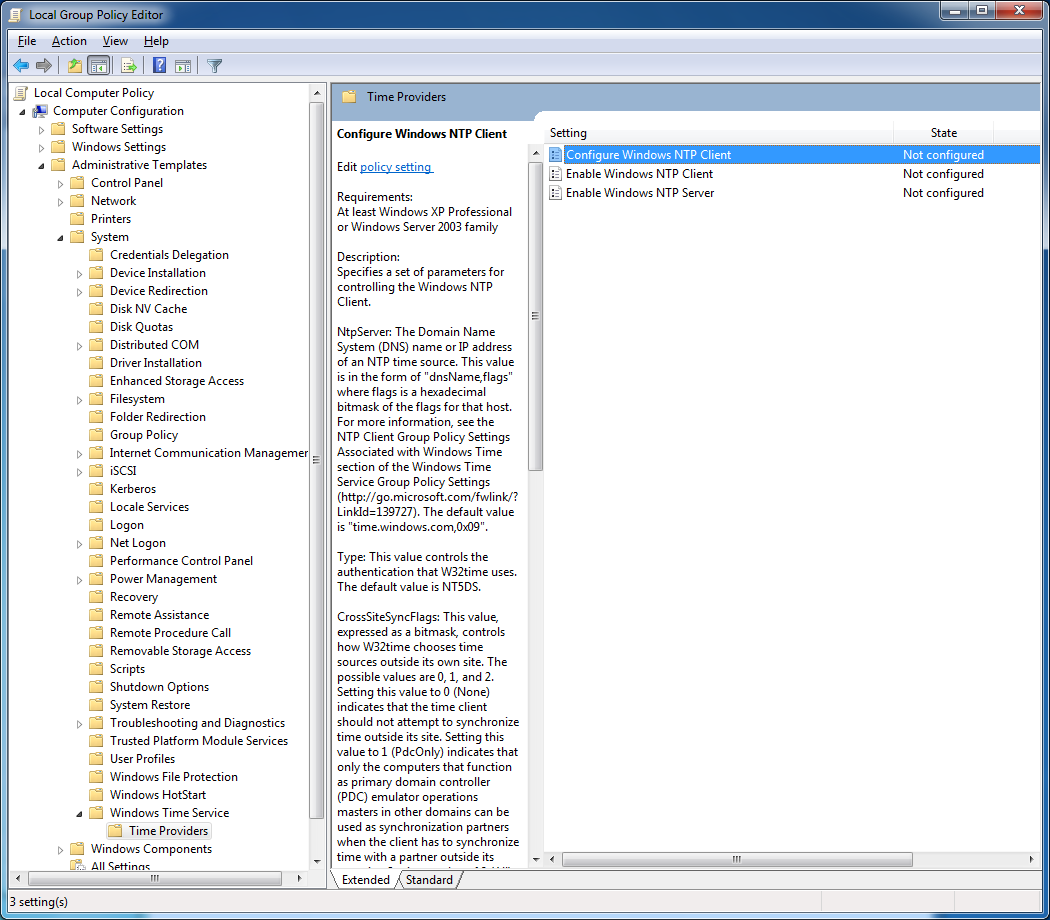
Here you will find two entries: The Global Configuration Settings and (in the Time Providers folder) settings for the Windows NTP client configuration, the setting to Enable Windows NTP Client and the setting to Enable Windows NTP Server.
Global Configuration Settings
This dialog allows three settings: Not Configured (you do not use the configuration), Enabled (the settings are valid) or Disabled (the service is not used). You can also enter a comment.
In addition, the dialog provides a number of options.
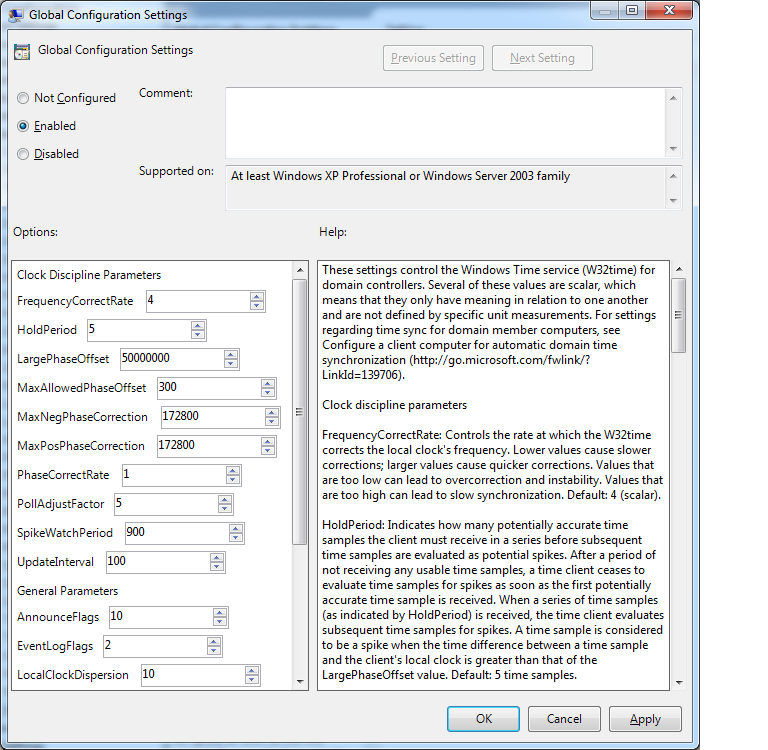
The following explanations are excerpts from the Windows 7 help.
These settings control the Windows Time service (W32time) for domain controllers. Several of these values are scalar, which means that they only have meaning in relation to one another and are not defined by specific unit measurements. For settings regarding time sync for domain member computers, see Configure a client computer for automatic domain time synchronization (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139706).
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
FrequencyCorrectRate |
Controls the rate at which the W32time corrects the local clock's frequency. Lower values cause slower corrections; larger values cause quicker corrections. Values that are too low can lead to overcorrection and instability. Values that are too high can lead to slow synchronization. Default: 4 (scalar) |
|
HoldPeriod |
Indicates how many potentially accurate time samples the client must receive in a series before subsequent time samples are evaluated as potential spikes. After a period of not receiving any usable time samples, a time client ceases to evaluate time samples for spikes as soon as the first potentially accurate time sample is received. When a series of time samples (as indicated by HoldPeriod) is received, the time client evaluates subsequent time samples for spikes. A time sample is considered to be a spike when the time difference between a time sample and the client's local clock is greater than that of the LargePhaseOffset value. Default: 5 time samples |
|
LargePhaseOffset |
Specifies the time variation from the client's local clock (phase offset) that a time sample must have to be considered a spike. Time samples that have time variations larger than the LargePhaseOffset value are considered spikes Default: 50,000,000 100-nanosecond units (ns), which is 5 seconds. |
|
MaxAllowedPhaseOffset |
Controls how W32time corrects the clock based on the size of the calculated time variation between the time sample and the client's local clock. If a response is received that has a time variation that is larger than this value, W32time sets the client's local clock immediately to the time that is accepted as accurate from the Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. If the time variation is less than this value, the client's local clock is corrected gradually. Default: 300 seconds |
|
MaxNegPhaseCorrection |
Controls the maximum allowable clock correction that can be made in a reverse direction. If a time sample is received that indicates a time in the past (as compared to the client's local clock) that has a time difference that is greater than the MaxNegPhaseCorrection value, the time sample is discarded. If this happens, the Windows Time source logs an event in the System log of Event Viewer. Default: 172,800 seconds |
|
MaxPosPhaseCorrection |
Controls the maximum allowable clock correction that can be made in a forward direction. If a time sample is received that indicates a time in the future (as compared to the client's local clock) that has a time difference greater than the MaxPosPhaseCorrection value, the time sample is discarded. Default: 172,800 seconds |
|
PhaseCorrectRate |
Controls how quickly W32time corrects the client's local clock difference to match time samples that are accepted as accurate from the NTP server. Lower values cause the clock to correct more slowly; larger values cause the clock to correct more quickly. Default: 7 (scalar) |
|
PollAdjustFactor |
Controls how quickly W32time changes polling intervals. When responses are considered to be accurate, the polling interval lengthens automatically. When responses are considered to be inaccurate, the polling interval shortens automatically. Default: 5 (scalar) |
|
SpikeWatchPeriod |
Specifies the amount of time that suspicious time samples are received from a time source before these time samples are accepted as accurate. Time samples are considered suspicious when the time difference between the time sample and the client's local clock is larger than the value of LargePhaseOffset. SpikeWatchPeriod is used in conjunction with HoldPeriod to help eliminate sporadic, inaccurate time samples that are returned from a peer. Default: 900 seconds |
|
UpdateInterval |
Specifies the amount of time that W32time waits between corrections when the clock is being corrected gradually. When it makes a gradual correction, the service adjusts the clock slightly, waits this amount of time, and then checks to see if another adjustment is needed, until the correction is finished. Default: 100 1/100th second units, which is 1 second. |
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
AnnounceFlags |
A bitmask value that controls how time service availability is advertised through NetLogon. Default: 0x0a hexadecimal. For possible values, see Config\AnnounceFlags Entry (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139718). |
|
EventLogFlags |
Controls special events that may be logged to the Event Viewer System log. Default: 0x02 hexadecimal bitmask. For possible values, see NtpClient\EventLogFlags Subkey (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139720). |
|
LocalClockDispersion |
Indicates the maximum error in seconds that is reported by the NTP server to clients that are requesting a time sample. (Applies only when the NTP server is using the time of the local CMOS clock.) Default: 10 seconds |
|
MaxPollInterval |
Controls the maximum polling interval, which defines the maximum amount of time between polls of a peer. Default: 10 in log base-2, which is 1,024 seconds. (Should not be set higher than 15.) |
|
MinPollInterval |
Controls the minimum polling interval that defines the minimum amount of time between polls of a peer. Default: 6 in log base-2, which is 64 seconds. |
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ChainEntryTimeout |
Specifies the maximum amount of time that an entry can remain in the chaining table before the entry is considered to be expired. Expired entries may be removed when the next request or response is processed. Default: 16 seconds |
|
ChainMaxEntries |
Controls the maximum number of entries that are allowed in the chaining table. If the chaining table is full and no expired entries can be removed, any incoming requests are discarded. Default: 128 entries |
|
ChainMaxHostEntries |
Controls the maximum number of entries that are allowed in the chaining table for a particular host. Default: 4 entries |
|
ChainDisable |
Controls whether or not the chaining mechanism is disabled. If chaining is disabled (set to 0), the RODC can synchronize with any domain controller, but hosts that do not have their passwords cached on the RODC will not be able to synchronize with the RODC. Default: 0 Boolean. |
|
ChainLoggingRate |
Controls the frequency at which an event that indicates the number of successful and unsuccessful chaining attempts is logged to the System log in Event Viewer. Default: 30 minutes |
Additional information on settings can be found in "Appendix A: Technical Reference Topics" (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=128273).
Configuring the Windows NTP Client
The dialog for Windows NTP client configuration is similar to the Global Configuration dialog.
The two dialogs for enabling the Window NTP client or server essentially have only three options: Not Configured, Enabled and Disabled. If you enable the client the computer can synchronize its system clock with NTP servers. You can disable this service if you wish to use an external time provider. If you enable the server, the computer can service the NTP requests from other computers in the network.
However, there are fewer, different options here.
The following explanations are excerpts from the Windows 7 help.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
NtpServer |
The Domain Name System (DNS) or IP address of an NTP time source. This value is in the form of "dnsName,flags" where flags is a hexadecimal bitmask of the flags for that host. For more information, see the NTP Client Group Policy Settings Associated with Windows Time section of the Windows Time Service Group Policy Settings (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139727). The default value is "time.windows.com,0x09". |
|
Type |
This value controls the authentication that W32time uses. The default value is NT5DS. |
|
CrossSiteSyncFlags |
This value, expressed as a bitmask, controls how W32time chooses time sources outside its own site. The possible values are 0, 1, and 2. Setting this value to 0 (None) indicates that the time client should not attempt to synchronize time outside its site. Setting this value to 1 (PDC only) indicates that only the computers that function as primary domain controller (PDC) emulator operations masters in other domains can be used as synchronization partners when the client has to synchronize time with a partner outside its own site. Setting a value of 2 (All) indicates that any synchronization partner can be used. This value is ignored if the NT5DS value is not set. The default value is 2 decimal (0x02 hexadecimal). |
|
ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes |
This value, expressed in minutes, controls how long W32time waits before it attempts to resolve a DNS name when a previous attempt failed. The default value is 15 minutes. |
|
ResolvePeerBackoffMaxTimes |
This value controls how many times W32time attempts to resolve a DNS name before the discovery process is restarted. Each time DNS name resolution fails, the amount of time to wait before the next attempt will be twice the previous amount. The default value is 7 attempts. |
|
SpecialPollInterval |
This NTP client value, expressed in seconds, controls how often a manually configured time source is polled when the time source is configured to use a special polling interval. If the SpecialInterval flag is enabled on the NTPServer setting, the client uses the value that is set as the SpecialPollInterval, instead of the MinPollInterval and MaxPollInterval values, to determine how frequently to poll the time source. The default value is 3600 seconds (1 hour). |
|
EventLogFlags |
This value is a bitmask that controls events that may be logged to the System log in Event Viewer. Setting this value to 0x1 indicates that W32time will create an event whenever a time jump is detected. Setting this value to 0x2 indicates that W32time will create an event whenever a time source change is made. Because it is a bitmask value, setting 0x3 (the addition of 0x1 and 0x2) indicates that both time jumps and time source changes will be logged. |